Source: Content compiled by Semiconductor Industry Watch (ID: icbank) from lightreading, thanks.
Based on our review of U.S. semiconductor company disclosures filed with the U.S. Securities and Exchange
Commission (SEC), we have some data: Sales to China by some U.S. giants last year were nearly $22 billion
higher than in 2020.
However, according to China's overall figures, a full embargo would reduce the sales of the 11 big U.S.
chipmakers by about $74.7 billion, a figure equivalent to about 27 percent of their total revenue. Such
a steep drop could have an impact on U.S. jobs, as well as research and development spending on chip
technology - while China struggles to become self-sufficient and weighs its own penalties.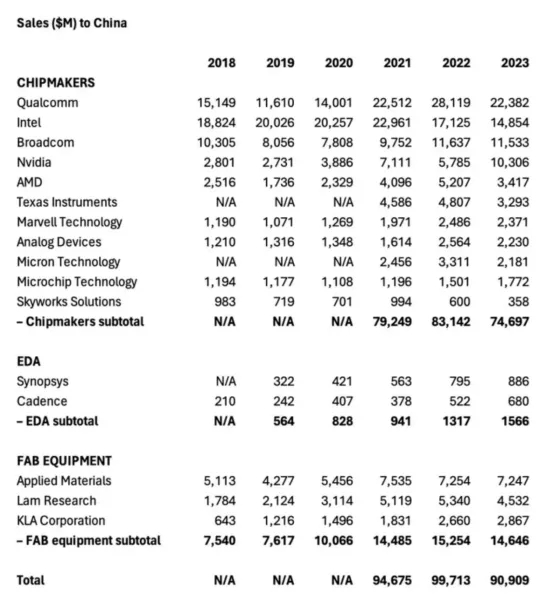
t can be seen from related reports that these measures could include restricting U.S. access to semiconductor
raw materials concentrated in China. At the same time, China appears to be waking up to the fact that sanctions
against China by U.S. authorities could do more harm to American companies. Ironically, if the Wall Street Journal
report published last week is accurate, it could put China's latest policy move squarely in line with the wishes of U.S.
hawks.
According to reports, China may not allow Chinese companies to buy American chips. Two of China's top three
telecom companies have reportedly been ordered to phase out all foreign processors by 2027.
American chipmakers also appear to be actively resisting the sanctions. Broadcom's sales in China reached $11.5
billion last year, up from just $7.8 billion in 2020. But the company clearly hopes the loss of Huawei as a customer
will be temporary. The U.S. export restrictions "require us to suspend sales to Huawei until we obtain permission
from the U.S. Department of Commerce." We may not be able to obtain or maintain the necessary permits to export
our products to them." And then described the government's actions as "restrictively" exporting to them.
Cadence and Synopsys, two U.S. developers of electronic design automation software, had nearly $1.6 billion in sales in
China last year, compared with $1.3 billion in 2022 and just $828 million in 2020. Applied Materials, Lam Research and
KLA's sales of fab equipment to China will reach $14.6 billion by 2023. That's down from $15.3 billion in 2022, but up
sharply from $10.1 billion in 2020.
ASML, a Dutch firm, has benefited from America's crazy restrictions. It is a global leader in UV-lithography, a technique
for imprinting chip patterns on silicon wafers, and a recognized monopoly in extreme ultraviolet lithography (EUV), which
is said to be the latest generation of technology needed to produce the most advanced chips. Under export controls
arranged by Wassenaar, the Dutch government prohibits the sale of EUV to China. But Chinese companies have been able
to acquire a slightly older technology from ASML called deep ultraviolet lithography (DUV).
The financial evidence in ASML's latest annual report is clear. ASML's sales in China amounted to 2.7 billion euros ($2.9 billion) in
2021 and 2.9 billion euros ($3.1 billion) in 2022, and last year, ASML's sales in China reached 7.3 billion euros ($7.8 billion) as
Zhongguo companies snapped up DUV equipment.